You are reading help file online using chmlib.com
|
You are reading help file online using chmlib.com
|
3.1 SAPI Compliance Required Tests
3.2 SAPI Compliance Feature List Tests
4 Using the compliance testing tool
6 Compliance Testing Configuration Options
6.1 SAPI 5.0 Compliance Testing Application Toolbar
6.2 SAPI 5.0 Compliance Testing Application Menu Choices
6.3 SAPI 5.0 Compliance Testing Logging Options
6.4 SAPI 5.0 Compliance Testing Run Options
6.5 SAPI 5.0 Compliance Test Selection Options
7.4 Compliance Test Customization
7.6 OS Language Incompatibility
8.5 OS Language Incompatibility
Table 1: Events Compliance Test
Table 2: Lexicon Compliance Test
Table 3: Command and Control Compliance Test
Table 4: Required Compliance Tests
Table 5: Events Feature Compliance Test
Table 6: Grammar Feature Compliance Test
Table 7: Feature Compliance Tests
Table 8: Sample Engine Required Compliance Test results
Table 9: Sample Engine Feature Compliance Test results
Table 10: Strings to be localized
Table 17: Sample Engine Required Test Results
Table 18: Sample Engine Feature List Test Results
Table 19: Strings to be localized for compliance tests
Table 21: Required Compliance Tests Failed
Table 22: Feature Compliance Tests Not Supported
This paper, directed toward engine vendors, describes the SAPI 5.0 compliance testing tool by answering the following questions:
· What does SAPI compliance for SAPI 5.0 imply?
· What are the SAPI compliance tests?
· What does each test look for?
The goals of the compliance tool are to help engine vendors test their speech engines for SAPI compliance and port these speech engines to SAPI 5.0. The tests also help vendors to support various SAPI features that are not required for compliance. These tests do not test the speech or performance quality of the engines. All compliance tests assume that SAPI will do parameter validation, and as such, they do not check the engine’s ability to handle invalid parameters such as null, bad pointers, or values out of range.
To run the compliance tests, the SPcomp.exe tool is used and either the Text-to-Speech (TTS) or the Speech Recognition (SR) test suite is selected. This tool generates a log report indicating the results of the compliance tests.
There are two types of SAPI 5 compliance tests:
1) required tests
2) feature list tests
The compliance tests do not necessarily test the DDI directly, instead, the use the SAPI API function calls to test the engine’s response to the DDI. The default engine is always used as the engine in the compliance test. Currently, the supported languages for the compliance tests are English, Japanese and Simplified Chinese[1]. Please check Microsoft® Speech.NET Technologies for language pack updates and information.
The results of the required tests are of a pass/fail nature. These tests were designed to help an engine reach a minimal amount of functionality with the SAPI DDI layer. In order to be SAPI compliant, the engine must pass all required SAPI tests.
The results of the feature list tests are either “Supported” or “Unsupported”. Feature list tests were designed to help engine vendors port advanced features to SAPI 5.0. To be SAPI compliant, the engine does not need to pass any feature list test, although it is recommended that all features be implemented if possible.
The minimum requirements for speech recognition for dictation are a 200 mhz Pentium with 64 MB for win 95/98 or 96 MB for NT. The recommended computer is a 300 Mhz Pentium II with 128 megs of RAM or better.
The SAPI 5.0 compliance test tool, SPcomp.exe, enables you to load compliance test suites and determine the test result logging options. Please see Compliance Tests for more options.
The SPcomp.exe test tool creates the .pro file for a given test suite. Perform compliance tests by starting the SPcomp.exe application and loading a test suite from a .pro file. The .pro file loads the associated dynamic link library (.dll), which contains the SR or TTS compliance tests.
To start the SAPI 5.0 compliance test tool SPcomp.exe from Windows Explorer, double-click the compliance tool icon. Alternatively, you can perform each compliance test from the command line by running the compliance test tool and command line syntax.
For example, the command line syntax for running the SRcomp compliance test in the srcompreq.pro test suite is as follows:
C:> SPcomp.exe srcompreq.proSPcomp.exe srcompreq.pro
Starts the compliance test tool and loads the speech recognition (SR) required tests from the SRcomp.dll.
SPcomp.exe srcompopt.pro
Starts the compliance test tool and loads the speech recognition (SR) feature list tests from the SRcomp.dll.
SPcomp.exe ttscompreq.pro
Starts the compliance test tool and loads the text-to-speech (TTS) required tests from the TTScomp.dll.
SPcomp.exe ttscompopt.pro
Starts the compliance test tool and loads the text-to-speech (TTS) feature list tests from the TTScomp.dll.
The SAPI 5.0 compliance tests verify that you have successfully implemented the required features to be considered compatible with SAPI 5.0. Your engine must successfully complete each of the following four compliance tests with 100 percent pass rate to be compliant with SAPI 5.0.
1. srcompreq.bat
—Speech Recognition (SR) required test batch file.
2. srcompopt.bat
—Speech Recognition (SR) feature list test batch file.
2. ttscompreq.bat
—Text-to-speech (TTS) required test batch file.
4. ttscompopt.bat
—Text-to-speech (TTS) feature list test batch file.
The SAPI 5.0 compliance tool generates a result log and you can configure it to display the result log information or you can save it to a file. The test result log contains pass or fail state information for each segment of the test suite. If a compliance test fails, you can review the result log to determine the origin of the failure.
Example result log with a 100% pass rate for all tests.
Total:============================================================================= PASS FAIL SUPPORTED UNSUPPORTED ABORTED SKIPPED----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 0 0 0 0=============================================================================Status: PASS
The SAPI 5.0 compliance test application user interface (UI) enables you to configure the testing options. The following section provides additional compliance test configuration information.
· SAPI 5.0 Compliance Testing Application Toolbar
· SAPI 5.0 Compliance Testing Application Menu Choices
· SAPI 5.0 Compliance Testing Logging Options
· SAPI 5.0 Compliance Testing Run Options
· SAPI 5.0 Compliance Test Selection Options
The main window of the SAPI 5.0 compliance testing application contains a toolbar from which you can access the configuration options. Additionally, the configuration options are also available from the menu bar located at the top of the compliance testing application window.
Pause on an icon to display tooltip text. Click an icon to view the information associated with the feature.
Load the test DLL
Loads a test dynamic-link library (DLL).
You can run compliance tests using one of the following methods:
1. From the SAPI Engine Compliance Tool, click File, and then click Load Test DLL.
2. Load
the test DLL into SPcomp.exe from the command line.
For more information, see Using
the compliance testing tool.
Note: loading a compliance test with either method results in automatically unloading any previously loaded compliance tests.
Load the test settings
Loads one of the pre-configured test suites.
You can run compliance tests using one of the following methods:
1. From the SAPI Engine Compliance Tool, click File, and then click Load Settings.
2. Load
the test DLL into SPcomp.exe from the command line.
For more information, see Using
the compliance testing tool.
Note: loading a compliance test with either method results in automatically unloading any previously loaded compliance tests.
Save settings
Saves the configuration settings for the compliance test application.
Copy
Selects and copies content from the display log.
Clear Window
Clears the display contents of the result log.
Find
Searches for a specific word or phrase within the result log.
Find Next
Searches for the next occurrence of a specific word or phrase within the result log.
Run Test
Begins the compliance test.
Stop Test
Stops the compliance test.
Set Run Options
Configures the compliance test options.
Select Tests
Chooses which compliance test contained in the test suite to.
Set Logging
Determines location of the compliance test log information.
The SAPI 5.0 compliance testing application configuration choices are accessible through the menu system. The following items are covered in this section:
· File menu
· Edit menu
· Test menu
· Options menu
· Help menu
Click File to set configuration options to load settings, save settings, or load the appropriate test DLL. Use the arrow keys to view various menu choices. Press ENTER to select a menu choice.
Click Edit to copy text from the result log and search for text within the result log. Use the arrow keys to view various menu choices. Press ENTER to select a menu choice.
Click Test to run the test or select a test. Use the arrow keys to view various menu choices. Press ENTER to select a menu choice.
Click Options to view the various configuration settings. Use the arrow keys to view various menu choices. Press ENTER to select a menu choice.
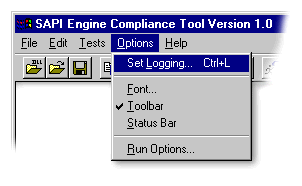
Click Help and then click About to display the SAPI 5.0 Engine Compliance Tool Version dialog box. Use the arrow keys to view the various menu choices. Press ENTER to select a menu choice.
From the Options menu, choose Logging Settings to set SAPI 5.0 compliance test result log configuration options.
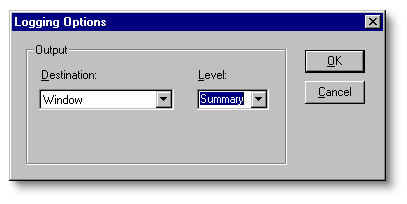
Window
Displays the test result information in the main window of the compliance testing application.
Log File
Saves the test result information as text in a log file.
The log file is located at the same directory as SPcomp.exe tool and the file name will be the following style:
spcomp@442.logThe numbers "442" in the file name are generated by the SPcomp.exe tool and will be incremented by one each time you restart SPcomp.exe tool and run the test. A new log file is generated each time you start SPcomp.exe tool and run a compliance test.
Detailed
Specifies detailed result log information.
Summary
Specifies summary result log information.
From the Options menu, click Run Options to configure SAPI 5.0 compliance testing run options.
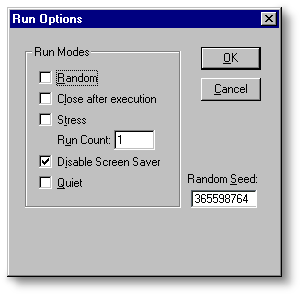
Random
Randomizes the test order.
Close after execution
Closes the compliance testing application after the test sequence.
Stress
This option should not be selected for compliance tests.
Run count
Specifies the number of interactions the selected test should run.
Disable screen saver
Disable the screen saver.
Quiet
Runs the selected test in quiet mode.
Random Seed
The random seed value set here is used for the next time you run the compliance test.
Note: When troubleshooting a failed compliance test, you need to enter the same seed value information that was used for the failed compliance test before you repeat the compliance test procedure.
You can obtain the compliance test seed value from the "Random Seed" field information in the SPcomp@xxx.log file that was generated during the unsuccessful compliance test.
From the Test menu, click Select Test to configure SAPI 5.0 compliance test choices.
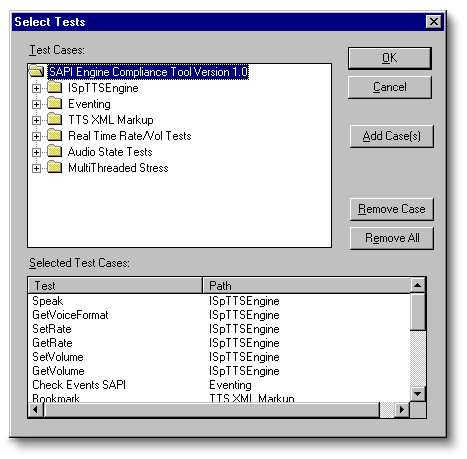
Test Cases
Displays the current test suite.
Selected Test Cases
Displays the current selected tests.
Add Case(s)
Adds test items to the list of
selected test cases.
Alternatively, to add test cases, right-click the test case in the test case
display window and click Add Item.
![]()
Remove Case
Removes the selected test case from the current test. However, removing the selected test does not affect the need to successfully pass this test case to satisfy SAPI compliancy.
Alternatively, to remove test cases, right-click the test cases in the selected test case display window and click Remove Case.

Remove All
Removes all test cases.
SAPI compliant SR engines must be able to perform the following[2]:
§ Generate certain SR events
§ Interact with the SAPI lexicon
§ Handle Command and Control (C&C) grammars
§ Generate Phrase Elements
§ Support auto pause on recognition
§ Support rule synchronization
§ Support multiple instances of the engine
§ Support multiple application contexts
Events will be checked for with .wav files. The test will feed the wav file to the engine and expect a specific event notification to occur. Please note that whether or not the engine can fire a specific event depends on the confidence threshold of the engine. Engine vendors could change the .wav quality to meet their requirement.
For English:
|
Test |
Description |
Resource IDs |
Description |
|
SoundStart |
Test will check if a sound start event occurs. |
IDS_WAV_SOUNDSTART |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav |
|
IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Input CFG grammar |
||
|
SoundEnd |
Test will check if a sound end event occurs. |
IDS_WAV_SOUNDEND |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav |
|
IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Input CFG grammar |
||
|
PhraseStart |
A .wav file with audio the engine can do recognition on. Test insures that a phrase start event occurs |
IDS_WAV_PHRASESTART IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
Recognition |
A .wav with audio that the engine can do recognition on. Test insures that a recognition event occurs. |
IDS_WAV_RECOGNITION_1 IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
False Recognition |
A wav file and a mismatching C&C grammar are loaded. Test insures that false recognition event occurs. |
IDS_WAV_RECOGNITION_1 IDR_RULE_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
SoundStart/ SoundEnd |
Test will check that the sound start event occurs before the sound end event. |
IDS_WAV_SOUNDSTARTEND IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
PhraseStart/ Recognition |
Test will check that the phrasestart event occurs before the recognition event. |
IDS_WAV_RECOGNITION_1 IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
SoundStart/ PhraseStart/ Recognition/ SoundEnd/ |
A wav file with audio that the engine can do recognition on. Test insures that the audiooffsets of these events are correct in terms of value comparison. |
IDS_WAV_RECOGNITION_1 IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav Input CFG grammar |
Table 1: Events Compliance Test
It is expected that changes in the user and application lexicon will be synchronized with the engine both when the engine starts up and after it has loaded a command and control grammar.
|
Test |
Description |
Resource IDs |
Description |
|
User Lexicon Before C&C Grammar Loaded |
A made-up word with its customized pronunciation is added to the user lexicon. After command and control grammar is loaded, audio will be sent with the word added and the expected result is checked for. |
IDS_WAV_SYNCH_BEFORE_LOAD IDR_SNORK_GRAMMAR IDS_RECO_SYNCH_BEFORE_LOAD IDS_RECO_NEWWORD_PRON |
Input .wav file, lexicon.wav Input CFG grammar The lexicon form of new word The pronunciation of the new word in user lexicon |
|
User Lexicon After C&C Grammar Loaded |
After command and control grammar is loaded, a made-up word with its customized pronunciation is added to the user lexicon. Audio will be sent with the word added and the expected result is checked for. |
IDS_WAV_SYNCH_AFTER_GRAM IDR_SNORK_GRAMMAR IDS_RECO_SYNCH_AFTER_GRAM IDS_RECO_NEWWORD_PRON |
Input .wav file, lexicon.wav Input CFG grammar The lexicon form of new word The pronunciation of the new word in user lexicon |
|
Application Lexicon and C&C Grammar |
A made-up word with its customized pronunciation is added to the application lexicon. After command and control grammar is loaded, audio will be sent with the word added and the expected result is checked for. |
IDS_WAV_APPLEX IDR_SNORK_GRAMMAR IDS_APPLEX_WORD IDS_APPLEX_PROP
|
Input .wav file, lexicon.wav Input CFG grammar The lexicon form of new word The pronunciation of the new word in application lexicon |
|
User lexicon before application lexicon |
A made-up word is added to both user lexicon and application lexicon using the different customized pronunciations. After command and control grammar is loaded, audio will be sent with the word’s pronunciation in user lexicon and the expected result is checked for. |
IDS_WAV_USERLEXBEFOREAPPLEX IDR_SNORK_GRAMMAR IDS_USERLEXBEFOREAPPLEX_WORD IDS_USERLEXBEFOREAPPLEX_USERPROP IDS_USERLEXBEFOREAPPLEX_APPPROP |
Input .wav file, lexicon.wav Input CFG grammar The lexicon form of new word The pronunciation of the new word in user lexicon The pronunciation of the new word in application lexicon |
Testing the engine for grammar compliance is perhaps the most complex set of tests. The engine must process a grammar correctly. Each test will use a grammar specifically tailored for the particular feature.
|
Test |
Description |
Resource IDs |
Description |
|
L Tag |
A three-element list grammar is loaded. Audio with the middle item to be recognized with the sent to the engine and the result checked for this item. |
IDS_RECO_L_TAG IDS_WAV_L_TAG IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Expected Result Input .wav file, tag_l.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
Expected Rule |
A grammar with two identical rules is loaded. The first rule will be activated. Audio that triggers this rule is sent and test verifies that the engine uses the first rule. The first rule is then de-activated and the second rule is activated. The same audio is sent and the test verifies that the engine uses the second rule. |
IDS_RECO_EXPRULE_FIRSTRULE IDS_RECO_EXPRULE_SECONDRULE IDS_WAV_EXPRULE_TAG IDR_EXPRULE_GRAMMAR |
First Rule’s Name Second Rule’s Name Input .wav file, tag_exprule.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
P Tag |
A simple grammar with a single phrase. Audio is sent and recognition is expected. Audio that does not contain the phrase is sent and no recognition is expected. |
IDS_RECO_P_TAG IDS_WAV_P_TAG IDR_P1_GRAMMAR |
Expected Result Input .wav file, tag_p.wav Input CFG grammar
|
|
O Tag |
A grammar will be defined with a phrase and an optional phrase preceding and following it. Three audio streams will be sent. One with the first optional phrase, one for the second, and the third that does not contain any optional phrases. The appropriate recognition result is checked for in each case. |
IDS_RECO_O_TAG_1 IDS_RECO_O_TAG_2 IDS_RECO_O_TAG_3 IDS_WAV_O_TAG_1 IDS_WAV_O_TAG_2 IDS_WAV_O_TAG_3 |
FirstOptionalWord Required word Second Optional word Input .wav file containing the first optional word, tag_o1.wav Input .wav file containing the second optional word, tag_o2.wav Input .wav file without optional words, tag_o3.wav |
|
RULEREF Tag |
A grammar with a phrase with a rule reference and a rule defined will be loaded. Audio that triggers the rule will be sent and the result checked. |
IDS_RECO_RULE_TAG IDS_WAV_RULE_TAG IDR_RULE_GRAMMAR |
Expected Result Input .wav file, tag_rule.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
/Disp/lex/pron format |
Test ensures engine can support customized pronunciation provided in the command and control grammar file. |
IDS_CUSTOMPROP_NEWWORD_PRON IDS_CUSTOMPROP_NEWWORD_DISP IDS_CUSTOMPROP_NEWWORD_LEX IDS_CUSTOMPROP_RULE IDS_WAV_CUSTOMPROP |
The customized pronunciation form of the new word The customized display form of the new word The customized lexicon form of the new word The dynamic grammar rule name Input .wav file, lexicon.wav |
Table 3: Command and Control Compliance Test
|
Test |
Description |
Resource IDs |
Description |
|
Phrase Elements |
The audio offsets of SPPHRASEELEMENTs in one SPPHRASE are correctly filled in, which means that the audio offset of the first SPPHRASEELEMENT is less than the audio offset of the second SPPHRASEELEMENT, the audio offset of the second SPPHRASEELEMENT is less than the third one, etc. |
IDS_WAV_RULE_TAG IDR_RULE_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_rule.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
Auto Pause |
The test makes sure engine can support auto pause feature provided by SAPI. |
IDS_AUTOPAUSE_DYNAMICWORD1 IDS_AUTOPAUSE_DYNAMICWORD2 IDS_AUTOPAUSE_DYNAMICRULE1 IDS_AUTOPAUSE_DYNAMICRULE2 IDS_WAV_AUTOPAUSE |
The word in the first rule The word in the second rule The name of the first rule The name of the second rule Input .wav file, autopause.wav |
|
Top-level rule invalidation |
Test verifies that engine can synchronize the rule information after SAPI notifies engine of top-level rule invalidation. |
IDS_INVALIDATETOPLEVEL_DYNAMICWORDS IDS_INVALIDATETOPLEVEL_DYNAMICRULE IDS_WAV_INVALIDATETOPLEVEL_OLD IDS_INVALIDATETOPLEVEL_DYNAMICNEWWORDS IDS_WAV_INVALIDATETOPLEVEL_NEW |
The words in the dynamic grammar The rule name in the dynamic grammar Input .wav file used before invalidation, tag_exprule.wav The new words in the dynamic grammar Input .wav file used after invalidation |
|
None-top-level rule invalidation |
Test verifies that engine can synchronize the rule information after SAPI notifies engine of non-top-level rule invalidation. |
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_RULE1 IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_RULE2 IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_TOPLEVELRULE IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_OLDWORD1 IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_OLDWORD2 IDS_WAV_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_OLD IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_NEWWORD1 IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_NEWWORD2 IDS_WAV_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_NEW |
The first rule name The second rule name The top-level rule name The word in the first rule used before invalidation The word in the second rule used before invalidation Input .wav file used before invalidation, tag_exprule.wav The word in the first rule used after invalidation The word in the second rule used after invalidation Input .wav file used after invalidation, tag_rule.wav |
|
Multiple recognition contexts |
Multiple recognition contexts will be created with different grammars. The test will verify that the recognition event is generated by the correct recognition contexts. |
IDS_RECO_P_TAG IDS_WAV_MULT_RECO IDR_P1_GRAMMAR IDR_P2_GRAMMAR |
The result expected in the second grammar Input .wav file, multireco.wav The first grammar used by the first recocontext The second grammar used by the second recocontext |
|
Multiple recognition engine instances |
Basic tests are run separately on different threads to see if engine can support multi instances. |
NA |
NA |
Some of the features exposed through SAPI are useful from a competitive advantage point of view. Features are not required by SAPI compliance, but may be an attractive function for engine vendors to implement. SAPI features are:
§ Interference and hypothesis events
§ Dictation functionalities
§ Advanced command and control features
§ Command and control alternate
§ Engine properties
§ Inversed text normalization
Events will be checked for with .wav. The test will feed the .wav to the engine and expect a specific event notification to occur. Please note that whether or not the engine can fire a specific event depends on the confidence threshold of the engine. Engine vendors may change the .wav files if it is felt that the .wav quality does not meet their requirements (Refer to Section 7.4).
|
Test |
Description |
Resource IDs |
Descriptions |
|
Interference |
A wav file with noises. Test will check that an interference event occurs. |
IDS_WAV_INTERFERENCE IDR_L_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_l.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
Hypothesis |
A .wav file with audio that engine can do recognition on. Test insures a hypothesis event occurs. |
IDS_WAV_HYPOTHESIS IDR_EXPRULE_GRAMMAR |
Input .wav file, tag_exprule.wav Input CFG grammar |
Table 5: Events Feature Compliance Test
This the required features if Engine wants to support dictation grammar. This include some basic functionalities for dictation grammar. This includes lexicon, dictation tag, dictation alternates.
|
Test |
Description |
Resource IDs |
Descriptions |
|
User Lexicon Before dictation Grammar Loaded |
A made-up word with its customized pronunciation is added to the user lexicon. After dictation grammar is loaded, audio will be sent with the word added and the expected result is checked for. |
IDS_WAV_SYNCH_BEFORE_LOAD IDS_RECO_SYNCH_BEFORE_LOAD IDS_RECO_NEWWORD_PRON |
Input .wav file, lexicon.wav The lexicon form of new word The pronunciation of the new word in user lexicon |
|
User Lexicon After dictation Grammar Loaded |
After dictation grammar is loaded, a made-up word with its customized pronunciation is added to the user lexicon. Audio will be sent with the word added and the expected result is checked for. |
IDS_WAV_SYNCH_AFTER_DICT IDS_RECO_SYNCH_AFTER_DICT IDS_RECO_NEWWORD_PRON |
Input .wav file, lexicon.wav The lexicon form of new word The pronunciation of the new word in user lexicon |
|
Dictation Tag |
A rule with dictation tag is loaded. Audio is feed and the test verifies the recognition event is generated. |
IDS_DICTATIONTAG_WORDS IDS_DICTATIONTAG_RULE IDS_WAV_DICTATIONTAG |
The word before the dictation tag The dynamic grammar rule name Input .wav file, tag_exprule.wav |
|
Dictation alternates |
Test ensures that engine can generate alternate results for dictation grammar. The test makes sure that engine has its own alternate object and the object can generate some alternate results. |
IDS_WAV_EXPRULE_TAG |
Input .wav file, tag_exprule.wav |
Table 5: Dictation Compliance Test
Each test will use a grammar specifically tailored for the particular feature. Some tests would use dynamic grammar instead of the static grammar.
|
Test |
Description |
Resource IDs |
Descriptions |
|
|
WildCard Tag |
A rule with wildcard tag is loaded. Audio is feed and the test verifies the recognition event is generated. |
IDS_WILDCARD_WORDS IDS_WILDCARD_RULE IDS_WAV_WILDCARD
|
The word before the wildcard tag The dynamic grammar rule name Input .wav file, tag_rule.wav |
|
|
TextBuffer Tag |
A grammar with <TextBuffer> tag will be loaded. Test fills in the content of TextBuffer on the fly. Audio with both static part and dynamic part of the grammar would be feed and the result would be checked. |
IDS_CFGTEXTBUFFER_WORDS IDS_CFGTEXTBUFFER_BUFFERWORD IDS_CFGTEXTBUFFER_RULE IDS_WAV_CFGTEXTBUFFER |
The words before TEXTBUFFER tag The word for TEXTBUFFER tag The rule name Input .wav file, tag_exprule.wav |
|
|
Use the correct grammar |
Two unambiguous grammars are loaded to test if engine can use the correct grammar to do recognition. |
IDS_RECO_RULE_TAG IDS_WAV_RULE_TAG IDR_L_GRAMMAR IDR_RULE_GRAMMAR |
Expected result for the second grammar Input .wav file, tag_rule.wav The first grammar The second grammar |
|
|
Use the most recently activated grammar |
Two ambiguous grammars are loaded to test if engine can use the most recently activated grammar to do the recognition. |
IDS_WAV_RULE_TAG IDR_RULE_GRAMMAR
|
Input .wav file, tag_rule.wav Input CFG grammar |
|
Table 6: Grammar Feature Compliance Test
|
Test |
Description |
Resource IDs |
Descriptions |
|
Command and Control alternates |
Test ensures that the engine can generate alternate results for command and control grammar |
IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_BESTWORD IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_ALTERNATE1 IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_ALTERNATE2 IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_WORDS IDS_WAV_ALTERMATESCFG |
The best choice of the CFG grammar Alternate word in CFG grammar Alternate word in CFG grammar Others words in the CFG grammar tag_exprule.wav |
|
Engine numeric properties |
If engine supports the numeric properties specified by SAPI |
NA |
|
|
Engine text properties |
If engine can return S_FALSE on the text properties that are not supported. |
NA |
|
|
Inversed Text Normalization |
The test uses a wav file and expects engine to pass back a result containing digits together with the normal result. Please note that this is a very specific ITN test and is not coverage of ITN related issues. |
IDS_RECO_GETITNRESULT IDS_WAV_GETITNRESULT IDR_RULE_GRAMMAR |
Expected ITN result Input .wav file, tag_rule.wav Input CFG grammar |
The sample engine is not fully SAPI compliant due to the fact that it does not have the full range of functionality that a true SR engine would have. Table 8 indicates which compliance tests will pass. Table 9 indicates which features are supported.
|
Test |
Result |
Description |
|
Events |
|
|
|
SoundStart |
Pass |
|
|
SoundEnd |
Pass |
|
|
PhraseStart |
Pass |
|
|
FalseRecognition |
Fail |
The sample engine doesn’t generate this event based on the real SR job. |
|
Recognition |
Pass |
|
|
SoundStart/SoundEnd order |
Pass |
|
|
PhraseStart/Recognition order |
Pass |
|
|
Event offset |
Pass |
|
|
Lexicon |
|
|
|
User Lexicon Before C&C Grammar Loaded |
Fail |
The sample engine doesn’t use user lexicon. |
|
User Lexicon After C&C Grammar Loaded |
Fail |
The sample engine doesn’t use user lexicon. |
|
App Lexicon |
Fail |
The sample engine doesn’t use application lexicon. |
|
Use user lexicon before application lexicon |
Fail |
The sample engine does not use either a user lexicon or an application lexicon. |
|
Grammar |
|
|
|
L Tag |
Fail |
The result might be sometimes fail and sometimes pass. The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
Expected Rule |
Pass |
|
|
P Tag |
Fail |
The result might be sometimes fail and sometimes pass. The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
O Tag |
Fail |
The result might be sometimes fail and sometimes pass. The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
Ruleref Tag |
Fail |
The result might be sometimes fail and sometimes pass. The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
/Disp/lex/pron format |
Fail |
The result might be sometimes fail and sometimes pass. The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
Other |
|
|
|
Phrase Elements |
Pass |
|
|
Auto Pause |
Pass |
|
|
Top-level rule invalidation |
Fail |
The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
Non-top-level rule invalidation |
Fail |
The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
Multiple recognition contexts |
Pass |
|
|
Multiple recognition engine instances |
|
The sample engine randomly generates a cfg result based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
Table 8: Sample Engine Required Compliance Test results
|
Test |
Result |
Description |
|
Events |
|
|
|
Hypothesis |
SUPPORTED |
|
|
Interference |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine doesn’t generate the event correctly. |
|
Dictation |
|
|
|
User lexicon synchronize before dictation grammar loaded |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine doesn’t use user lexicon. |
|
User lexicon synchronize after dictation grammar loaded |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine doesn’t use user lexicon. |
|
Dictation Tag |
SUPPORTED |
|
|
Dictation alternates |
SUPPORTED |
|
|
Grammar |
|
|
|
Wildcard Tag |
SUPPORTED |
|
|
TextBuffer Tag |
SUPPORTED |
|
|
Use the correct grammar |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
Use the most recently activated grammar |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine randomly generates results based on the given grammar. It doesn’t do any real recognition. |
|
Other |
|
|
|
Command and Control alternates |
UNSUPPORTED |
The compliance test only uses one rule while the sample engine needs at least two rules. |
|
Engine numeric properties |
SUPPORTED |
|
|
Engine text properties |
SUPPORTED |
|
|
Inversed Text Normalization |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine doesn’t have this functionality. |
Table 9: Sample Engine Feature Compliance Test results
Many of the tests do require that a specific recognition result be returned to verify proper handing of such things as the grammar format. To accommodate different engines variability with recognition of different voices and to support non-English engines, these tests will enable the engine vendor to supply a sound file that passes the test (Refer to Section 7.5). Since some tests might share the same .wav file, it is recommended to supply a .wav file with different name. Additionally the grammars can be changed to accommodate words that the engine is able to recognize better (Refer to Section 7.6).
The compliance tests will tests engines for the supported languages[3]. To test an SR engine that uses another language, one must:
§ Ensure that the correct language pack is installed. For Windows 2000 and Millennium Edition, this may be done by installing the language pack from the Windows 2000 or Windows Millennium CD. For Windows 98 and Windows NT 4.0, install the language pack from the Windows Update web site.
§ Select the engine as the default engine using Speech Recognition tab in Speech properties.
§ Create and insert a string table in the sapi5sdk\tools\comp\sr\srcomp.rc that is localized for the language. (Refer to Table 10)
§ Create the .wav files[4] according to the new string table and place this under the specified directory (according to the search path precedence (Refer to Section 7.5.2)).
§ Create and compile the appropriate XML files using a grammar editor and complier.
§ Include the CFG binaries into the .dll by importing the CFG file names into srcomp.rc[5].
§ Recompile the sr.dsp.
§ Run the compliance tests.
If you want to add resource for test SoundStart for language 888:
1. create and insert copy a string table in srcomp.rc for language 888.
2. Change the string “IDS_WAV_SOUNDSTART” to the new .wav file you want to use.
3. Insert the xml grammar file you want to use into the project. Modify the IDR_L_GRAMMAR reference to your cfg binary.
NOTE: If the default engine supports multiple languages, then the compliance test will only run on the first language specified in string “Language” under key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Speech\Recognizers\Tokens\MSASREnglish\Attributes. In other words you need to change the order of the languages in the attributes key under your speech recognizer token for each language you wish to test. (Refer to Section 7.6)
The strings that need to be localized are shown in Table 10.
|
String Number |
English Text |
|
|
IDS_RECO_L_TAG |
put |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_EXPRULE_TAG_1 |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_EXPRULE_TAG_2 |
the |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_P_TAG |
white |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_O_TAG_1 |
please |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_O_TAG_2 |
walk |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_O_TAG_3 |
slowly |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_RULE_TAG |
seven |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_LN_TAG |
red |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_NEWWORD_PRON |
s n ao 1 r k |
Translate phonemes |
|
IDS_AUTOPAUSE_DYNAMICWORD1 |
put |
Translate string |
|
IDS_AUTOPAUSE_DYNAMICWORD2 |
red |
Translate string |
|
IDS_AUTOPAUSE_DYNAMICRULE1 |
Action |
Translate string |
|
IDS_AUTOPAUSE_DYNAMICRULE2 |
color |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATETOPLEVEL_DYNAMICWORDS |
play the oboe |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATETOPLEVEL_DYNAMICRULE |
Play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATETOPLEVEL_DYNAMICNEWWORDS |
please play the seven |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_RULE1 |
option |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_RULE2 |
Thing |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_TOPLEVELRULE |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_OLDWORD1 |
empty |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_OLDWORD2 |
Oboe |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_NEWWORD2 |
Seven |
Translate string |
|
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_TOPLEVELWORDS |
Play the |
Translate string |
|
IDS_CFGTEXTBUFFER_WORDS |
Play the |
Translate string |
|
IDS_CFGTEXTBUFFER_BUFFERWORD |
oboe |
Translate string |
|
IDS_CFGTEXTBUFFER_RULE |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_BESTWORD |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_ALTERNATE1 |
played |
Translate string |
|
IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_ALTERNATE2 |
pay |
Translate string |
|
IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_WORDS |
The oboe |
Translate string |
|
IDS_ALTERNATESCFG_RULE |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_RECO_GETITNRESULT |
please play the 7 |
Translate string |
|
IDS_CUSTOMPROP_NEWWORD_PRON |
s n ao 1 r k |
Translate phonemes |
|
IDS_CUSTOMPROP_RULE |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_CUSTOMPROP_NEWWORD_DISP |
abc |
Translate string |
|
IDS_CUSTOMPROP_NEWWORD_LEX |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_DICTATIONTAG_WORDS |
Play the |
Translate string |
|
IDS_DICTATIONTAG_RULE |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_WILDCARD_WORDS |
Please play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_WILDCARD_RULE |
play |
Translate string |
|
IDS_APPLEX_PROP |
s n ao 1 r k |
Translate phonemes |
|
IDS_USERLEXBEFOREAPPLEX_USERPROP |
s n ao 1 r k |
Translate phonemes |
|
IDS_USERLEXBEFOREAPPLEX_APPPROP |
P l ey |
Translate phonemes |
|
IDS_INVALIDATENONTOPLEVEL_NEWWORD1 |
Please |
Translate string |
Table 10: Strings to be localized
The compliance tests use a search path precedence to find the various .wav files needed for the compliance tests. The order of search is:
§ current directory
§ ‘..\resources’,
§ ‘..\..\..\resources’
§ ‘..\..\resources’
If the compliance tests cannot find the .wav files in these directories, the test will pop up a dialog asking the user to enter the customized dir to open the file. The new directory will be added to the search order and the new search order will persist for the life of SpComp.
It is important to note that for languages that do not have a SAPI standard phoneme set (i.e. languages which are not supported in this version of SAPI), the engine will fail the following required compliance tests:
|
Test |
Result |
|
Lexicon |
|
|
User Lexicon Before C&C Grammar Loaded |
Fail |
|
User Lexicon After C&C Grammar Loaded |
Fail |
|
App Lexicon |
Fail |
|
Use user lexicon before application lexicon |
Fail |
|
User lexicon synchronize before dictation grammar loaded |
Fail |
|
User lexicon synchronize after dictation grammar loaded |
Fail |
|
/Disp/lex/pron format |
Fail |
The compliance tests are not based on the language of the OS. They are based on the first language in the token of the default engine. In other words, a Japanese engine on an English OS will cause the compliance tests to load the Japanese resources and run the compliance tests expecting a Japanese engine. In order to run the compliance test for an engine that has a different language than the OS, you will need to set the default engine on the Speech Recognition tab in Speech properties.
NOTE: If the default engine supports multiple languages, then the compliance test will only run the first language. In other words you need to change the order of the languages in the attributes key under your speech recognizer token for each language you wish to test. For example, if your engine token supports both Japanese and English, to test English, , the string “Language” must be like “409; 411” under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Speech\Recognizers\Tokens\MSASREnglish\Attributes
To test Japanese, the string “Language” must be like “411; 409” under the same key.
SAPI compliant TTS engines must be able to perform the following:
§ Speak with SAPI defined speak flags
§ Return the supported audio output formats
§ Interact with the SAPI lexicon
§ Interpret SAPI XML tags
§ React to programmatic volume changes
§ React to programmatic rate changes
§ Synthesize certain SAPI events
§ Skip forward and backward through a segment of text
§ Support multiple instances
The speak tests test the engine ability to interact with ISpTTSEngine::Speak as well as process and react to actions. Before SAPI passes a speak call to the engine, it Query Interfaces (QIs) the engine object for ISpTTSEngine and ISpObjectWithToken interfaces. If either of these are not implemented correctly, the speak call will fail. If both of the QIs pass, then SAPI will pass the speak call to the engine. The speak call contains a number of speak flags. Table 1 describes the individual tests.
|
Test |
Description |
|
SPF_DEFAULT |
This is the normal, default speak flag. The engine should be able to render text to the output site under normal conditions. The engine should also be able to continue rendering when passed the continue action from SAPI |
|
SPF_PURGEBEFORESPEAK |
The engine should be able to stop rendering when passed to abort action |
|
SPF_IS_XML |
The engine should be able to interpret the SAPI XML when passed to it by SAPI. |
|
SPF_ASYNC |
The engine should be able to render text to the output site. The asynchronous environment should not affect the engine since SAPI handles the multithreading issues. |
|
SPF_SPEAK_NLP_PUNC |
the engine should be able to speak punctuation. |
The compliance tests also test a number of combination scenarios to help ensure that the engine is able to stop speaking and start speaking in various combinations that are shown in table 2.
|
Test |
Description |
|
Speak Destroy |
SAPI sends the engine a speak call followed by an abort action. |
|
Speak Stop |
SAPI sends the engine a speak call followed by a purge call. This is to ensure that the engine is able to stop speaking and clear memory. |
The output format test checks to ensure that the engine is capable of passing its supported output format to SAPI. This is testing the ISpTTSEngine::GetOutputFormat function.
The lexicon tests check the interaction of the engine and SAPI. These tests add a word to the user and application lexicons and check to ensure that the engine is able to detect the words in the lexicon and is using the word pronunciation from the user lexicon first, and then the application lexicon second if the word is present in both lexicons. There are two separate tests as shown:
|
Test |
Description |
|
User lexicon |
A word is added to the user lexicon and the engine is requested to pronounce this word. The engine should be aware of the case sensitivity. The engine must support the SAPI phoneme, SAPI part of speech, as well the lexicon APIs. |
|
Application lexicon |
A word is added to the application lexicon and the engine is requested to pronounce this word. The engine must support the SAPI phoneme, SAPI part of speech, as well the lexicon APIs. |
The SAPI XML tags are required for compliance. The tags tests shown are required:
|
Test |
Description |
|
Bookmark |
Tests if the engine is able to process the bookmark tag and write the appropriate bookmark event. |
|
Silence |
Tests if the engine outputs the correct amount of silence as indicated by the silence tag. |
|
Volume |
Tests if the engine can change the volume by the correct amount. |
|
Spell |
Tests if the engine can handle the tag and spell out the text. |
|
Pron |
Tests if the engine can handle the SAPI defined phoneme set. |
|
Rate |
Tests if the engine can change the rate by the correct amount. |
|
Pitch |
Tests if the engine can change the pitch by the correct amount. |
|
Context |
Tests if the engine can handle the SAPI defined context tag. |
|
Engine proprietary SAPI tags |
Test if the engine can handle non-SAPI tags. |
This test checks to see if the engine is capable of processing the volume change action. When the engine received this action, it should call the GetVolume function from SAPI to get the new volume, and reflect the change in the audio output.
This test checks to see if the engine is capable of processing the rate change action. When the engine received this action, it should call the GetRate function from SAPI to get the new volume, and reflect the change in the audio output.
The events test checks to ensure that the engine is writing the correct data, especially wParam and lParam, to the event structure. For the sentence boundary event, wParam is the character length of the sentence including punctuation in the current input stream being synthesized. lParam is the character position within the current text input stream of the sentence being synthesized. For the word boundary event, wParam is the character length of the word in the current input stream being synthesized. lParam is the character position within the current text input stream of the word being synthesized. Any leading and ending spaces will not be included in the length of the word or the sentence. There are three events which are required for SAPI compliance:
|
Test |
Description |
|
SPEI_TTS_BOOKMARK |
Checks the engine’s ability to properly fire bookmarks embedded in the text. |
|
SPEI_WORD_BOUNDARY |
Checks the engine’s ability to generate word boundaries given a segment of text. |
|
SPEI_SENTENCE_BOUNDARY |
Checks the engine’s ability to detect and generate sentence boundaries. |
This test examines the engine’s ability to interact with the skip action. Once the engine receives this action, it should call the ISpTTSEngineSite::GetSkipInfo function. After it has completed the skip, it should call the ISpTTSEngineSite::CompleteSkip function.
The multiple instances test checks to ensure that the engine can handle multiple calls at the same time from SAPI. The tests contains a total of 4 threads and each thread has its own ISpVoice object and the test runs a random combination of the following tests 20 times consecutively:
§ Speak
§ Skip
§ GetOutPutFormat
§ SetRate
§ SetVolume
§ Check SAPI required Event
§ XML Bookmark
§ XML Silence
§ XML Spell
§ XML Pron
§ XML Rate
§ XML Volume
§ XML Pitch
§ Real time Rate changes
§ Real time Volume changes
§ Speak Stop
§ Lexicon
§ XML context
§ Engine proprietary SAPI tags and other combination of XML tags
Some of the features exposed through SAPI are useful from a competitive advantage point of view. Features are not required by SAPI compliance, but may be an attractive function for engine vendors to implement. SAPI features are:
§ Generation of phoneme events (determines if the engine can generate a phoneme event for a given string of text. The phonemes must correspond to the SAPI defined phonemes).
§ Generation of viseme events (determines if the engine can generate a viseme for a given string of text. The viseme must correspond with the SAPI defined visemes).
§ XML emphasis tag (the engine should change the volume, rate, or pitch of the audio rendered).
§ XML PartOfSp tag (the engine should handle the SAPI defined part of speech – the engine will need to implement this for the lexicon compatibility tests)
The sample engine is not fully SAPI compliant due to the fact that it does not have the full range of functionality that a true TTS engine would have. Table 6 indicates which compliance tests will pass. Table 7 indicates which features are supported.
|
Test |
Result |
Description |
|
Speak |
|
|
|
SPF_DEFAULT |
Pass |
|
|
SPF_PURGEBEFORESPEAK |
Pass |
|
|
SPF_IS_XML |
Pass |
|
|
SPF_ASYNC |
Pass |
|
|
SPF_SPEAK_NLP_PUNC |
Pass |
|
|
Speak Destroy |
Pass |
|
|
Speak Stop |
Pass |
|
|
GetOutput Format |
Pass |
|
|
Lexicon |
|
|
|
User Lexicon |
Fail |
The sample engine does not use a lexicon. |
|
App Lexicon |
Fail |
The sample engine does not use an application lexicon. |
|
XML Tags |
|
|
|
Bookmark |
Pass |
|
|
Silence |
Pass |
|
|
Volume |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot adjust the volume of the .wav files. |
|
Spell |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recorded .wav files and cannot spell each word. |
|
Pron |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recorded .wav files and cannot interpret the SAPI phonemes. |
|
Rate |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot adjust the rate of the .wav files. |
|
Pitch |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot adjust the pitch of the .wav files. |
|
Context |
Pass |
|
|
Engine proprietary SAPI tags |
Pass |
|
|
SetVolume |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot adjust the rate of the .wav files. |
|
SetRate |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot adjust the volume of the .wav files. |
|
Events |
|
|
|
SPEI_TTS_BOOKMARK |
Pass |
|
|
SPEI_WORD_BOUNDARY |
Pass |
|
|
SPEI_SENTENCE_BOUNDARY |
Pass |
|
|
Skip |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot skip sentences since it does not have a sentence breaker. |
|
Multiple Instances Test |
Fail |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot skip sentences, change rate, pitch, and volume, or use lexicons. |
Table 17: Sample Engine Required Test Results
|
Test |
Result |
Description |
|
Phoneme events |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot synthesize the phoneme events. |
|
Viseme events |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot synthesize the viseme events. |
|
XML Emph Tag |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot adjust the emphasis of the .wav files. |
|
XML PartOfSp |
UNSUPPORTED |
The sample engine uses pre-recoded .wav files and cannot adjust the part of speech of the .wav files. |
Table 18: Sample Engine Feature List Test Results
To test an engine that uses language aside for the supported languages, one must:
§ Ensure that the correct language pack is installed. For Windows 2000 and Millennium Edition, this may be done by installing the language pack from the Windows 2000 or Windows Millennium CD. For Windows 98 and Windows NT 4.0, install the language pack from the Windows Update web site.
§ Select the engine as the default engine using the TTS tab in Speech properties.
§ Create a string table in the \sapi5sdk\tools\comp\tts\ttscomp.rc which is localized for the language. (Refer to Table 19)
o Go to ResourceView in the ttscomp workspace, right click the mouse on “String Table”, and select “Insert Copy”. The following window will appear. From the window, select the language that the engine supports, and then click OK.
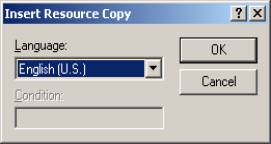
o Open \sapi5sdk\tools\comp\tts\ttscomp.rc to your editor and edit your language resources (Refer to Table 19), and then save ttscomp.rc
o The following is an example how to support GetOutputFormat test in Korean using Microsoft FrontPage editor:
§ Open ttscomp.dsw and create a string table in Korean, save ttscomp.rc
§ Go to below table 19 and find strings used in GetOutputFormat test. Only one string, IDS_STRING65, is found corresponding to the test.
§ Open ttscomp.rc in Notepad and find IDS_STRING65 under Korean resources
§ Launch Microsoft FrontPage and select File | New and Normal tab
§ Translate “This is the TTS Compliance Test” to Korean.
§ Select Preview tab, right click your mouse, select Encoding | Western European (Windows), and then cut/paste the string from MS FrontPage to IDS_STRING65 under Korean resources in your notepad
§ Save ttscomp.rc
§ Recompile the tts.dsp.
§ Run the compliance tests.
The strings that need to be localized are:
|
Test Name |
String Number |
English Text |
|
|
Speak Destroy |
IDS_STRING6 |
This is a long string of text that will not complete because it will be released it in the next line of code. The engine is expected to clean-up correctly and not fault. |
Translate string |
|
Speak
|
IDS_STRING8 |
Hello <BOOKMARK MARK= “12”>World |
Translate “Hello World” |
|
IDS_STRING10 |
This is a test. |
Translate string |
|
|
IDS_STRING11 |
Blah blah … |
May need to translate if engine does not understand phonemes |
|
|
Phoneme & Viseme Events |
IDS_STRING10 |
|
|
|
SetVolume
|
IDS_STRING10 |
|
|
|
SetRate |
IDS_STRING10 |
|
|
|
Check SAPI required Events
|
IDS_STRING20 |
Bookmark <BOOKMARK MARK= “123”/>test |
Translate “Bookmark test” |
|
XML Bookmark |
IDS_STRING20 |
|
|
|
XML Silence
|
IDS_STRING23 |
Hello World |
Translate string |
|
IDS_STRING24 |
Hello <SILENCE MSEC = “8000”/> World |
Translate “Hello World” |
|
|
XML Spell
|
IDS_STRING26 |
<SAPI> ENGLISH LANGUAGE</SAPI> |
May need to translate “ENGLISH LANGUAGE” if letters are not known (Refer to IDS_STRING27) |
|
IDS_STRING27 |
<SPELL> ENGLISH LANGUAGE </SPELL> |
May need to translate “ENGLISH LANGUAGE” if letters are not known |
|
|
XML Rate
|
IDS_STRING30 |
<RATE SPEED= ‘-5’> hello world </RATE> |
Translate “hello world” |
|
IDS_STRING31 |
<RATE SPEED= ‘5’> hello world </RATE> |
Translate “hello world” |
|
|
XML Volume
|
IDS_STRING33 |
<VOLUME LEVEL = ‘100’> hello </VOLUME> |
Translate “hello” |
|
IDS_STRING34 |
<VOLUME LEVEL = ‘1’> hello </VOLUME> |
Translate “hello” |
|
|
XML Pitch
|
IDS_STRING37 |
<PITCH MIDDLE =’-10’> a </PITCH> |
Translate the letter ‘a’ |
|
IDS_STRING38 |
<PITCH MIDDLE =’+10’> a </PITCH> |
Translate the letter ‘a’ |
|
|
XML PartOfSp
|
IDS_STRING48 |
H l ow |
Translate phonemes |
|
IDS_STRING52 |
N ow n p r ow n ow aa aa ah ao aw b ch eh er |
Translate phonemes |
|
|
IDS_STRING76 |
test |
Translate “test” |
|
|
Real time volume change
|
IDS_STRING53 |
This <BOOKMARK MARK=’1234’/>string is used in the real time rate and volume tests. It’s rate and volume are adjusted mid stream. Engines should pick these changes up. |
Translate “This string is used in the real time rate and volume tests. It’s rate and volume are adjusted mid stream. Engines should pick these changes up.” |
|
Real time rate change |
IDS_STRING53 |
|
|
|
XML Pronounce
|
IDS_STRING56 |
A |
Translate the word “a” |
|
IDS_STRING57 |
<PRON SYM=”aa n th ow p ow l ow jh iy aa n th ow p ow l ow jh iy aa n th ow p ow l ow jh iy”>a</PRON> |
Translate phonemes |
|
|
Skip |
IDS_STRING63 |
<SAPI>one. Two. Three. Four. Five. Six. Seven. Eight. Nine. Ten. <BOOKMARK MARK=”123”/>bookmark event. One. Two. Three. Four. Five. Six. Seven. Eight. Nine. Ten. </SAPI> |
Translate “one. Two. Three. Four. Five. Six. Seven. Eight. Nine. Ten. Bookmark event. One. Two. Three. Four. Five. Six. Seven. Eight. Nine. Ten.” |
|
User Lexicon Test
|
IDS_STRING64 |
Computer |
Translate “computer” |
|
IDS_STRING71 |
dh aa n th ow p ow l ow jh iy aa n th ow p ow l ow jh iy aa n th ow p ow l ow jh ch ow ao ah ow ow p ow l ow jh ch ow ao ah ow |
Translate phonemes |
|
|
IDS_STRING76 |
|
|
|
|
IDS_STRING94 |
h eh l ow w er l d h eh l ow w er l d h eh l ow w er l d h eh l ow w er l d |
Translate phonemes |
|
|
GetOutputFormat |
IDS_STRING65 |
This is the TTS Compliance Test |
Translate “This is the TTS Compliance Test” |
|
XML Non-SAPI tags |
IDS_STRING67 |
<SOMEBOGUSTAGS> Non-SAPI tags test </SOMEBOGUSTAGS> |
Translate “Non-SAPI tags test” |
|
XML Emph
|
IDS_STRING68 |
<SAPI>Do you hear me?</SAPI> |
Translate “Do you hear me?” |
|
IDS_STRING69 |
<SAPI><EMPH>Do you hear</EMPH>me?</SAPI> |
Translate “Do you hear me?” |
|
|
App Lexicon Test |
IDS_STRING76 |
|
|
|
IDS_STRING94 |
|
|
|
|
XML Context
|
IDS_STRING99 |
<context id=’date_mdy’>12/21/99</context><context id=’date_mdy’>12.21.00</context> <context id=’date_mdy’>12-21-9999</context> |
May need to translate dates |
|
IDS_STRING100 |
<context id=’date_dmy’>21/12/00</context><context id=’date_dmy’>21.12.33</context><context id=’date_dmy’>21-12-1999</context> |
May need to translate dates |
|
|
IDS_STRING101 |
<context id=’date_ymd’>99/12/21</context><context id=’date_ymd’>99.12.21</context> <context id=’date_ymd’>1999-12-21</context> |
May need to translate dates |
|
|
IDS_STRING102 |
<context id=’date_ym’>99-12</context><context id=’date_ym’>1999.12</context><context id=’date_ym’>99/12</context> |
May need to translate dates |
|
|
IDS_STRING103 |
<context id=’date_my’>12-99</context><context id=’date_my’>12.1999</context><context id=’date_my’>12/99</context> |
May need to translate dates |
|
|
IDS_STRING104 |
<context id=’date_dm’>21.12</context> <context id=’date_dm’>21-12</context> <context id=’date_dm’>21/12</context>” |
May need to translate dates |
|
|
IDS_STRING105 |
<context id=’date_md’>12-21</context> <context id=’date_md’>12.21</context> <context id=’date_md’>12/21</context> |
May need to translate dates |
|
|
IDS_STRING106 |
<context ID = ‘date_year’> 1999</context> <context ID = ‘date_year’> 2001</context> |
May need to translate dates |
|
|
IDS_STRING107 |
<context id=’time’>12:30:10</context><context id=’time’>12:30</context><context id=’time’>1’21”</context> |
May need to translate times |
|
|
IDS_STRING108 |
<context id=’number_cardinal’>3432</context> |
May need to translate number |
|
|
IDS_STRING109 |
<context id=’number_digit’>3432</context> |
May need to translate number |
|
|
IDS_STRING110 |
<context id=’number_fraction’>3/15</context> |
May need to translate number |
|
|
IDS_STRING111 |
<context id=’number_decimal’>423.12433</context> |
May need to translate number |
|
|
IDS_STRING112 |
<context id=’phone_number’>(425)706-2693</context> |
May need to translate phone number |
|
|
IDS_STRING113 |
<context id=’currency’>$12312.90</context> |
May need to translate currency |
|
|
IDS_STRING116 |
<context ID = ‘address’>One Microsoft Way, Redmond, WA, 98052</context> |
May need to translate address |
|
|
IDS_STRING117 |
<context ID = ‘address_postal’> A2C 4X5</context> |
May need to translate postal address |
|
|
IDS_STRING118 |
<CONTEXT ID = ‘MS_My_Context’> text </CONTEXT> |
Translate “text” |
|
|
Multiple-Instance Test
|
IDS_STRING41 |
Hello <SILENCE MSEC = “%d”/> World |
Translate “Hello World” |
|
IDS_STRING43 |
<PRON SYM = “aa n th ow p ow l iw jh iy”> hello </PRON> |
Translate SYM phonemes and “hello” |
|
|
IDS_STRING44 |
<RATE SPEED = “%d”> hello </RATE> |
Translate “Hello” |
|
|
IDS_STRING45 |
<VOLUME LEVEL = ‘%d’> hello </VOLUME> |
Translate “Hello” |
|
|
IDS_STRING46 |
<PITCH MIDDLE = ‘%d’> hello </PITCH> |
Translate “hello” |
|
|
IDS_STRING8 |
Hello <BOOKMARK MARK= “12”>World |
Translate “Hello World” |
|
|
IDS_STRING27 |
|
|
|
|
IDS_STRING67 |
|
|
|
|
IDS_STRING76 |
|
|
|
|
IDS_STRING94 |
|
|
|
|
IDS_STRING119 |
|
|
It is important to note that for languages which do not have a SAPI standard phoneme set (i.e. languages which are not supported in this SAPI release), the engine will fail the following required compliance tests:
|
Test |
Result |
|
Lexicon |
|
|
User Lexicon |
Fail |
|
App Lexicon |
Fail |
|
XML Tags |
|
|
Pron |
Fail |
Table 21: Required Compliance Tests Failed
The engine will also fail the following feature tests:
|
Test |
Result |
|
Phoneme events |
UNSUPPORTED |
|
Viseme events |
UNSUPPORTED |
|
XML PartOfSp |
UNSUPPORTED |
Table 22: Feature Compliance Tests Not Supported
The compliance tests are not based on the language of the OS. They are based on the first language in the token of the default engine. In other words, a Japanese engine on an English OS will cause the compliance tests to load the Japanese resources and run the compliance tests expecting a Japanese engine. In order to run the compliance test for an engine that has a different language than the OS, you will need to set the default engine on the Speech Recognition tab of Speech properties.
[1] For SR Simplified Chinese, the .wav files, cfg files, and resources do not ship with the SAPI 5.0 SDK. To request these localized files, please send mail to sapi5@microsoft.com.
[2] All SR tests use the default recognition profile. To increase the accuracy of the tests, you may wish to change the .wav files used (Refer to Section 7.4) or train the recognition profile.
[3] The Simplified Chinese SR resource files, cfg files and .wav files are not included in the SAPI 5 SDK. Please e-mail sapi5@microsoft.com to obtain these files.
[4] These wav files MUST have different names than the original wav files. The new wav file names should be reflected in the string table.
[5] A basic assumption of the compliance tests is that the CFG files are included in the dll whereas the wav files are external.
You are reading help file online using chmlib.com
|